The many use cases of blockchain technology
With Bitcoin becoming history’s first-ever border-less, decentralized and trust-less public ledger characterized by its underlying blockchain technology, many industries around the world have been quick to join the revolution. The high-level use case of blockchain technology, however, is not limited to fintech and digital currencies, but to many sectors including business, government, cyber security and more.
These are just a few of the key blockchain technology applications:
Business use cases of blockchain technology
Healthcare
MedRec is a great example of how blockchain is looking to improve healthcare systems. According to MIT Media Lab, MedRec is “ a novel, decentralized record management system for EMRs that uses blockchain technology to manage authentication, confidentiality, accountability, and data sharing.”
Travel
Companies like Expedia.com and Priceline currently have a monopoly on the travel market, which leverages their business demands from airlines and hotel chains. The price difference trickles down to the consumer level, driving down their cost savings while decreasing revenues for suppliers. Winding Tree aims to bypass this nascent issue by creating a B2C marketplace, enabling airlines like Lufthansa to work directly with consumers.
Real Estate
Just as blockchain acts as a public ledger for cryptocurrencies, it can serve as an immutable public ledger for all home and land ownership records.
Energy
WePower, a blockchain-based green energy trading platform, enables green energy project financing as well as renewable energy investment and trade at scale. To do this, the company has created its own cryptocurrency, a token called WPR. Each token is equal to one kilowatt-hour of power produced that is tradable on the platform. By tokenizing green energy and putting it on a blockchain, WePower aims to make peer to peer energy trade accessible to anyone.

Governmental use cases of blockchain technology
Voting
Voter validity is a major concern around the globe, undermining the central tenets of democratic elections. A blockchain-based voting system can help to ensure voter registration and identification so votes cannot be tampered with at a future date.
Pete Martin, the CEO of mobile voting platform Votem, said the following to Government Technology about blockchain’s utility in voting: “Blockchain technology provides all of the characteristics you would want in a platform that is arguably the most important part of a democratic society; it’s fault-tolerant, you cannot change the past, you cannot hack the present, you cannot alter the access to the system, every node with access can see the exact same results, and every vote can be irrefutably traced to its source without sacrificing a voter’s vote anonymity. End to end verifiable voting systems will give the voter the ability to verify if their vote is correctly recorded and correctly counted, for instance, if a ballot is missing, in transit or modified, it can even be detected by the voter and caught before the election is over.”
Record management
Governmental processes are highly susceptible to corruption much to the detriment of its citizens. With the fool-proof encryption standards of blockchain technologies, record legitimacy can be increased, foregoing fraudulent entries and data tampering.
Taxes
Blockchain has the potential to streamline the process of filing taxes that is typically prone to human error by ensuring that irrefutable information is stored on a public ledger. “I think the blockchain is about openness: an open ledger and advancing trust. Tax payers see positives in it, because they see less cost, less payroll, and more efficiency. Tax authorities see it as having to pay fewer auditors and gaining more liquidity, because they’re getting money into the coffers faster so they can do the jobs they have to do,” says Channing Flynn, EY International Tax Partner & Global Technology Tax Leader.

Cyber Security use cases of blockchain technology
The biggest advantage of blockchain is the aspect of decentralization that removes the risk of a single point of failure. By creating a distributed ledger, there is little leeway for cyber attacks that have the potential to compromise a database with centralized records.

Financial use cases of blockchain technology
Coming back to fintech, blockchain technology will also help to streamline international payments and peer to peer (P2P) transactions through pioneering payments platforms like COTI. Currently, cross-border e-commerce and P2P payments are riddled with deficiencies including fraud, ineffective local payment solutions, high fees, false positives and low approval rates, particularly for the 2.5bn people living in the developing world today.
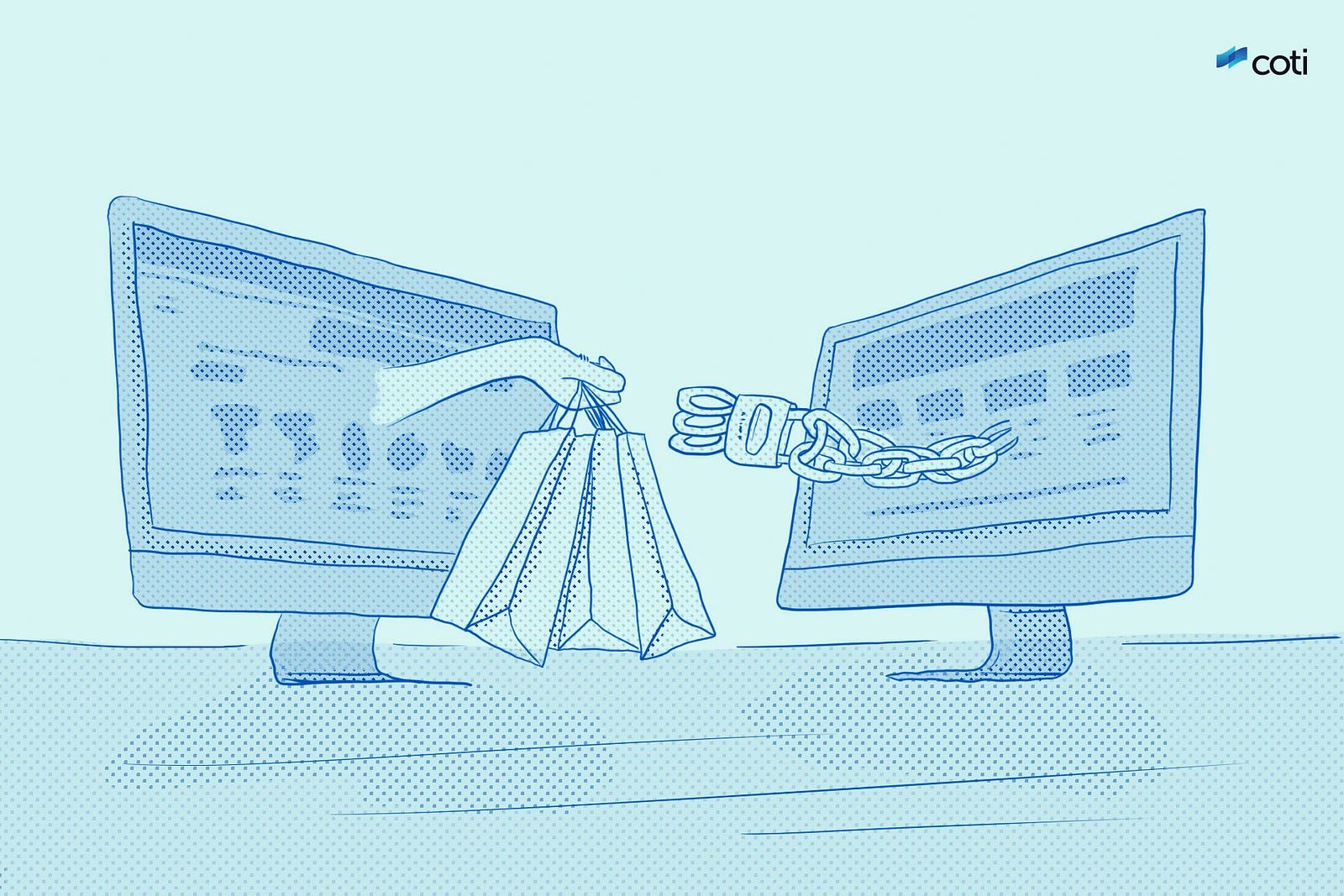

To open up the possibility for a lower friction payments experience, blockchain-based systems will secure transactions through cryptographic proof rather than trusted third-party intermediaries. The absence of a third party will also serve to drive down costs and increase approval rates so that every consumer with the capacity to pay is able to complete purchases.
Become a part of our growing community:




Original article and pictures take cdn-images-1.medium.com site
Комментариев нет:
Отправить комментарий